Insulin is a hormone that is naturally produced by the pancreas, and its primary function is to regulate blood sugar levels in the body. Insulin is used to treat people with diabetes, a chronic condition that affects the way the body processes blood sugar. There are several different types of insulin, each with its own unique characteristics, effects, and uses.
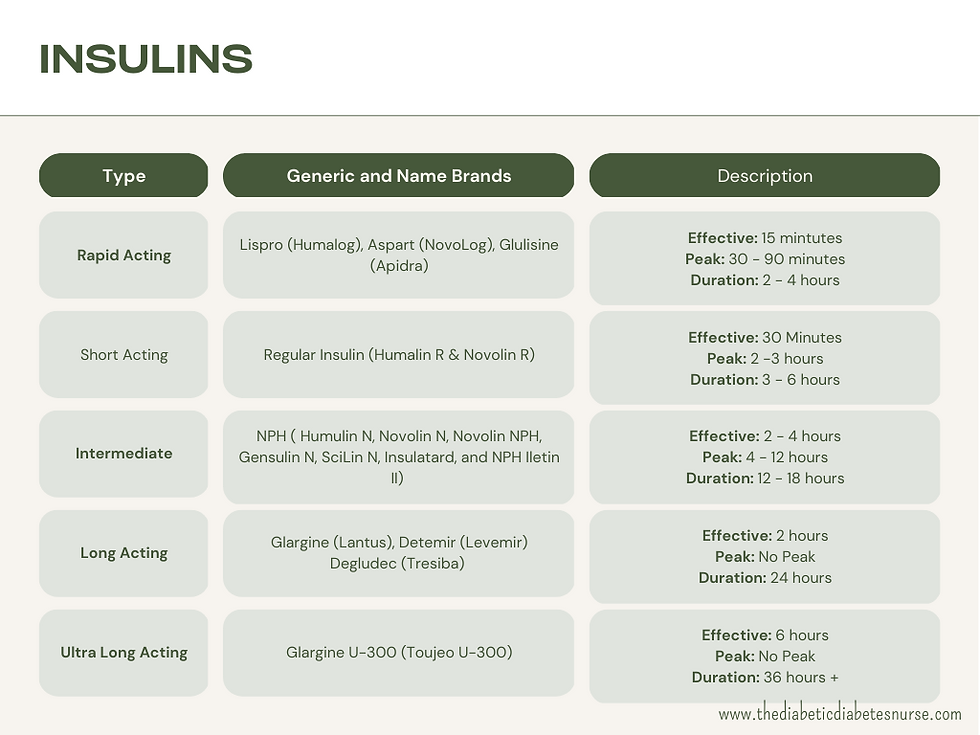
In 2014, inhaled insulin was FDA approved under the brand name Afrezza. Afrezza is the only approved inhaled insulin available. It is a rapid acting insulin. It starts working within 12 minutes, peaks within 30 minutes and lasts for 180 minutes.
The effects of insulin include lowering blood sugar levels by allowing the body's cells to take in glucose from the bloodstream and use it for energy. Insulin also helps to store excess glucose in the liver and muscles for later use.
Insulin is primarily used to treat diabetes. It is used to help manage blood sugar levels in people with type 1 diabetes, who cannot produce insulin on their own, as well as in people with type 2 diabetes, who may not produce enough insulin or may not use insulin efficiently. Insulin therapy can help reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications, such as nerve damage, kidney damage, and eye damage.
Insulin is a hormone that regulates glucose in the blood. It was first discovered in 1921 by Sir Frederick Banting and Charles Best, two Canadian scientists.
Prior to the discovery of insulin, people with diabetes had limited treatment options and often faced a grim prognosis. The only available treatments were low-carbohydrate diets and frequent injections of animal-derived pancreatic extracts. These treatments could provide temporary relief, but they were not sustainable or effective in the long term.
Banting and Best's discovery of insulin revolutionized the treatment of diabetes. They conducted experiments on dogs to demonstrate that they could extract insulin from the pancreas and use it to treat diabetes in the animals. Banting and Best received help from J.B. Collip and John Macleod in refining insulin into a pure state.
In 1922, they successfully treated a 14-year-old boy, Leonard Thompson, with severe diabetes with insulin extracted from the pancreas of a calf. Leonard Thompson lived for 13 more years with the help of insulin.
The discovery of insulin was hailed as a medical breakthrough, and Banting and Macleod were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1923. They shared the prize with their fellow colleagues Best and Collip. The production of insulin on a large scale began soon after the discovery, and people with diabetes were able to manage their condition and live longer, healthier lives.
Since then, insulin has undergone significant advancements in its development and production. The early insulin extracts were crude and had impurities that could cause allergic reactions in some people. Later, scientists developed purer forms of insulin and created different types of insulin with varying onset and duration times.
Today, insulin is produced synthetically using recombinant DNA technology, which allows for a more precise and pure product. It is available in various forms, including injectable insulin pens and pumps as well as inhaled insulin, making diabetes management more convenient and accessible for people with the condition.
References
American DIabetes Association. (2019, July 1). The History of a Wonderful Thing We Call Insulin | ADA. Diabetes.org. https://diabetes.org/blog/history-wonderful-thing-we-call-insulin
American Diabetes Association. (n.d.). Insulin basics | ADA. Diabetes.org. https://diabetes.org/healthy-living/medication-treatments/insulin-other-injectables/insulin-basics
CDC. (2021, March 25). Types of Insulin. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/type-1-types-of-insulin.html
Farinde, PharmD, PHD, A. (2020). Insulin Types: Types of Insulin. EMedicine. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/2172166-overview


Yorumlar